Stereomicroscope Vs Compound Light Microscope

Purchasing a microscope can exist the most heady matter when you lot build your classroom or abode laboratory. However, information technology could as well exist a confusing process for beginners. This commodity aims to provide you the necessary knowledge and to guide you through the decision process. Let'due south showtime hunting for the "Right" microscope for you!
We are talking virtually the "Light Microscope"
Earlier we first, I want to remind you that everything in this article refers to calorie-free microscopes (or optical microscopes), which is a microscope that includes a built-in light source. There are other types of microscopes, such equally fluorescence or electron microscope, but they are extremely expensive and typically used in scientific enquiry institutions. If you are interested in these advanced microscopes, check out the universities nigh you for their open-house or public science solar day.
By the way, a new product called a digital USB microscope is becoming more and more pop now. It is a completely different territory. We volition cover information technology after.
Chemical compound Microscope vs. Stereo Microscope
Basically, light microscopes use visible light to illuminate the specimen and to class the images. Based on the applications, calorie-free microscopes fall into ii main categories: the compound microscope and the stereo microscope. Therefore, the first stride of buying decision is to determine which types you demand. Below is a film of the chemical compound and stereo microscope.
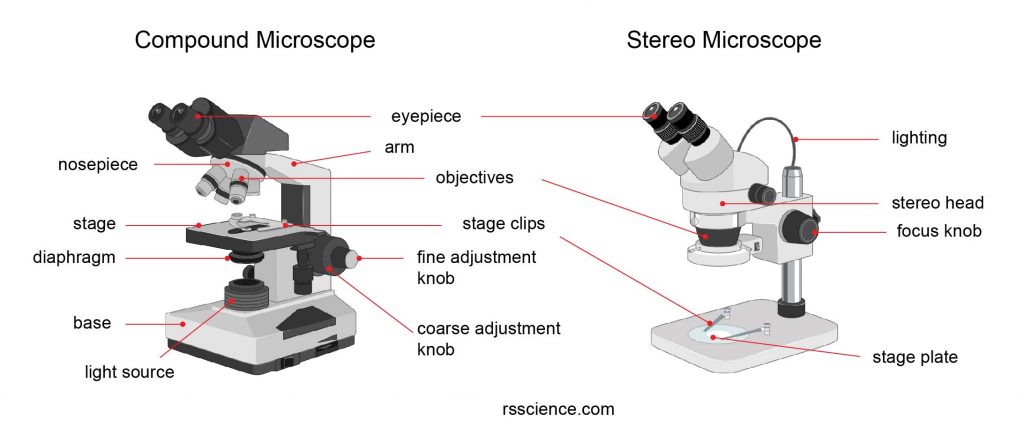
[In this figure] The compound microscope vs. stereo microscope.
What tin can nosotros see under a "Compound" microscope?
Compound microscopes (also referred to equally an upright lite microscope) are probably the almost common microscopes you tin can detect. Because the lite has to pass through the specimen, the ideal specimens for compound microscopes are small and sparse stuff.
Good examples are protozoa in the pond water, claret smear (blood cells), mouth swab (cheek cells), thin establish and tissue sections, pollens, cells, bacteria, semi-transparent water organisms (similar water bear or algae), and premade slide sets. Images below are examples using a compound microscope.
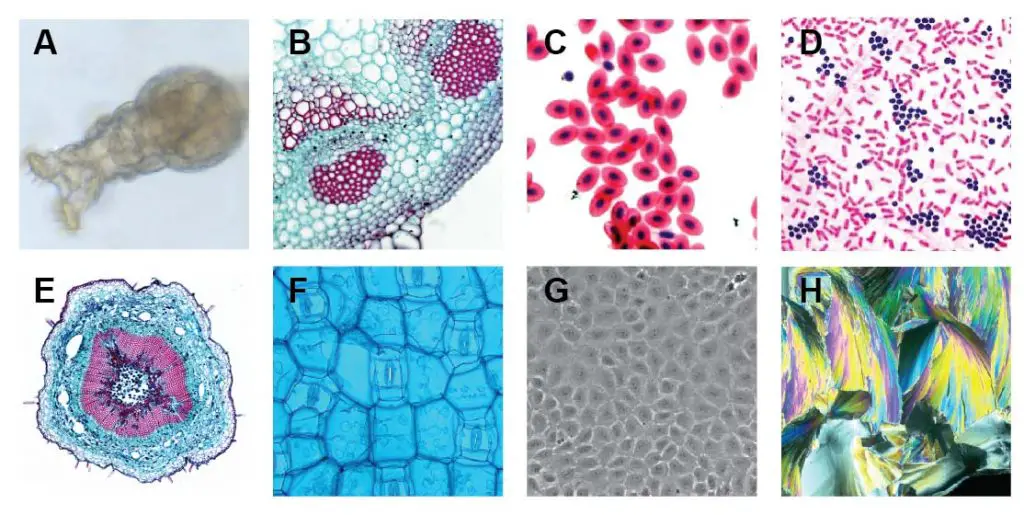
[ In this figure] Images using a compound microscope.
A. Rotifer (bright field); B. Helianthus stem (sparse stained department – bright field); C. Fish cherry blood cells (Stained – brilliant field); D. Leaner (Gram's Iodine stained – brilliant field); E. Loosen stalk (thin stained section – bright field + prototype stitching); F. Rhoeo Discolor leaf (brilliant field + blueish filter); G. Human cells cultivated in Petri dish (phase dissimilarity); H. Citric acid micro-crystal (polarized calorie-free).
In dissimilarity to the stereo microscopes, compound microscopes have a much college ability of magnification to run across the details of a subject. Therefore, compound microscopes are also known equally loftier power microscopes.
Typically, a compound microscope is supplied with three-5 objective lenses that range from 4x to 100x (4x/10x/40x/63x/100x). Assuming you have 10x eyepieces and 100x objective, the total magnification of this combination is i,000x (10×100 = k). By using special condensers, compound microscopes can also reach darkfield, phase contrast, polarized lite, or differential interference contrast (DIC) images for particular applications.
Things to consider when choosing a Compound microscope
1. Price
The microscope is a pretty mature market which means "you paid for what you get". Information technology is fair to say that the microscopes fabricated of plastics (below $30-40) are toys for children to have a sense of what science is.
For a beginner, a microscope with a metal arm and 3 objective lenses (around $100) could exist a proficient start. All the same, some microscopes in this range claim that they have 100x objective lenses and can be used to see tiny organisms such as bacteria. In fact, you lot may end upwardly with disappointing burr images due to the low resolution. (Hint: oil lens to solve resolution).
If you take microscopy equally a passionate hobby (and maybe yous desire to postal service some amazing pictures on your Facebook or Instagram), a solid compound microscope with a full metal body, a decent collection of objective lenses, a trinocular port for the camera, a mechanical stage for moving specimens, and an exchangeable condenser module could cost you lot more than than $300-1000.
Considering these high-end microscopes, I volition pay extra attention to the extensibility (the capability to upgrade co-ordinate to the potential futurity utilize) and subsequently-sale service. For microscopes used for a classroom, I will too consider the ease of maintenance and repairs.
2. Magnification
The quality of objective lenses determines the quality and price of a compound microscope. Thinking of what kind of specimen you will study the most and and so choose the suitable lens set. Typically, a descent chemical compound microscope (effectually $150-300) comes with at to the lowest degree 4 objective lenses (4x, 10x, 40x, 100x; usually a 100x lens is for oil immersion).
I will advise purchasing a microscope that is compatible with standard objectives and oculars, in case you desire to upgrade your lenses in the hereafter. There are more than technical considerations of objective lenses such as resolution and working altitude, which I volition write a more detailed article in the hereafter.
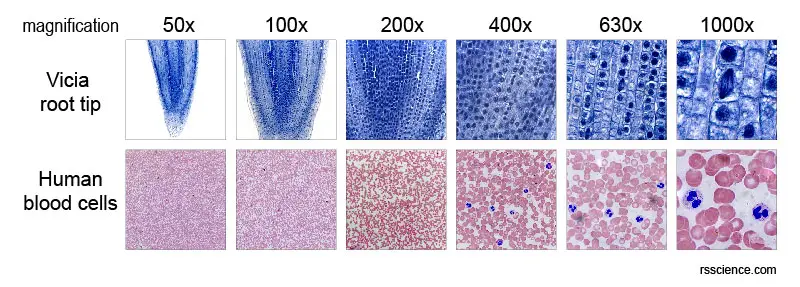
[In this figure] Looking at the same specimen from low to high magnifications.
The top raw is a serial of images of Vicia (pea family unit) root tip. At low magnifications (5x and 10x), you can have the overall view of the entire specimen. By getting closer (with higher magnification), you lot will start to notice the cells and their nuclei (blue dots). At high magnifications (63x and 100x with lens immersion oil), yous tin see some nuclei looked different from others. These spindle-shaped nuclei are dividing (or under mitosis) and their chromosomes (bundles of Deoxyribonucleic acid) are moving autonomously.
The bottom raw are images of man blood smear. At depression magnification, you may only be able to see many cerise particles (they are carmine blood cells and they don't have nuclei) everywhere. Merely while rotating the objective lens to at least higher than 40x, you can notice some cells are bigger and with nuclei (dark blue). Those are white blood cells. At 100x, you lot can meet very clearly the unique multi-segmented nuclei (night blue) and pink granules. Based on these features, nosotros tin conclude they are neutrophils, which protect our torso by engulfing leaner.
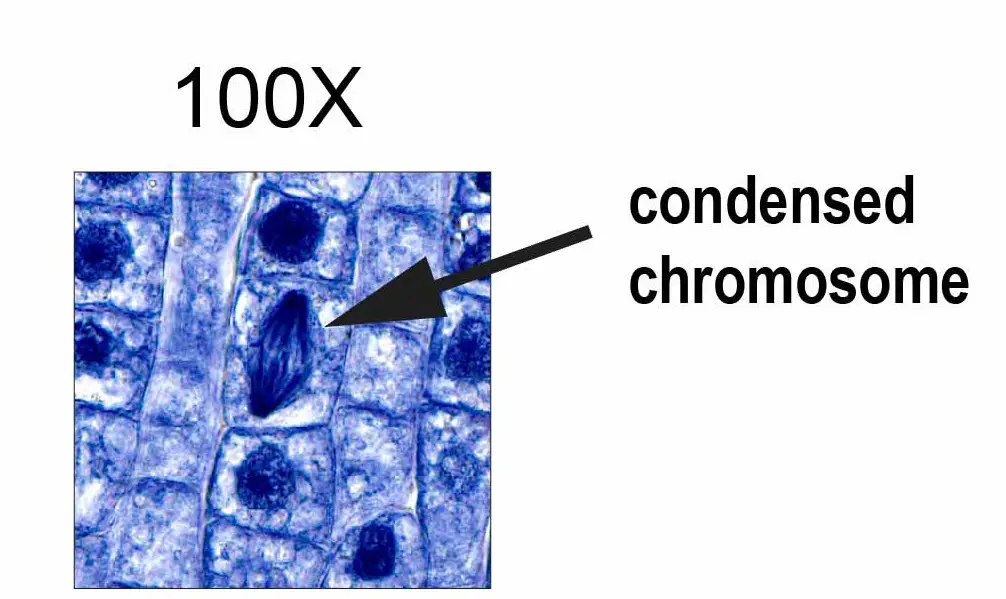
[In this figure] Spindle-shaped nuclei are diving (cell sectionalization).
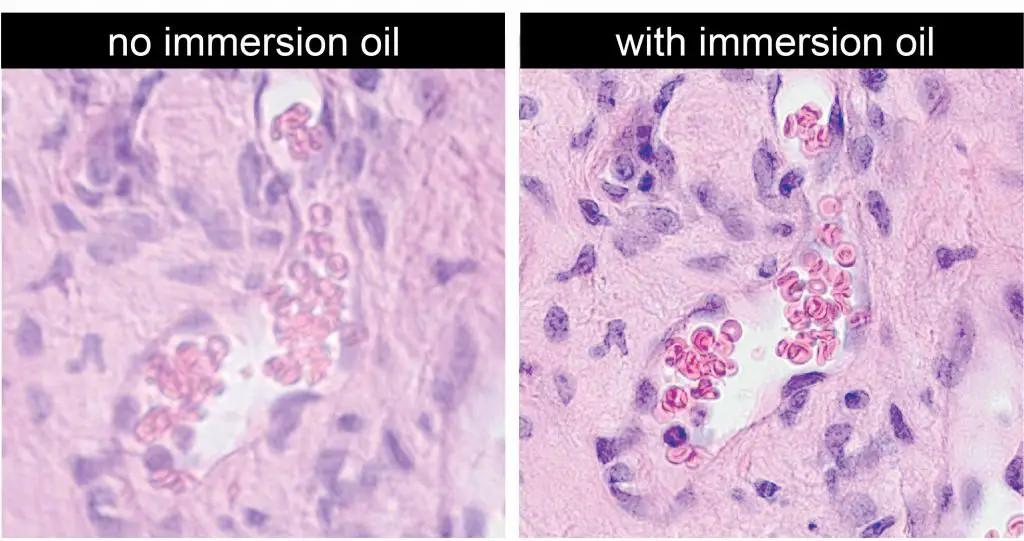
[In this effigy] Immersion oil increases the clarity of the image.
It is especially useful when you use a college magnification objective. For more than detail, please click here.
iii. Monocular, Binocular or Trinocular
The Monocular microscope has just 1 eyepiece and is usually found on the low-priced items. The Binocular microscope that allows you to see with both your eyes is the most pop and easy-to-use selection. Brand sure to choose the one with adjustable eyepieces because the distance between the two eyes is different for everyone. A Trinocular microscope has ii eyepieces similar a Binocular microscope and an boosted third eyetube for connecting a microscope camera. Usually, the Trinocular part is sectional for a high-end production. By using an adaptor or a camera/telephone holder, you may also take pictures on a Binocular microscope.
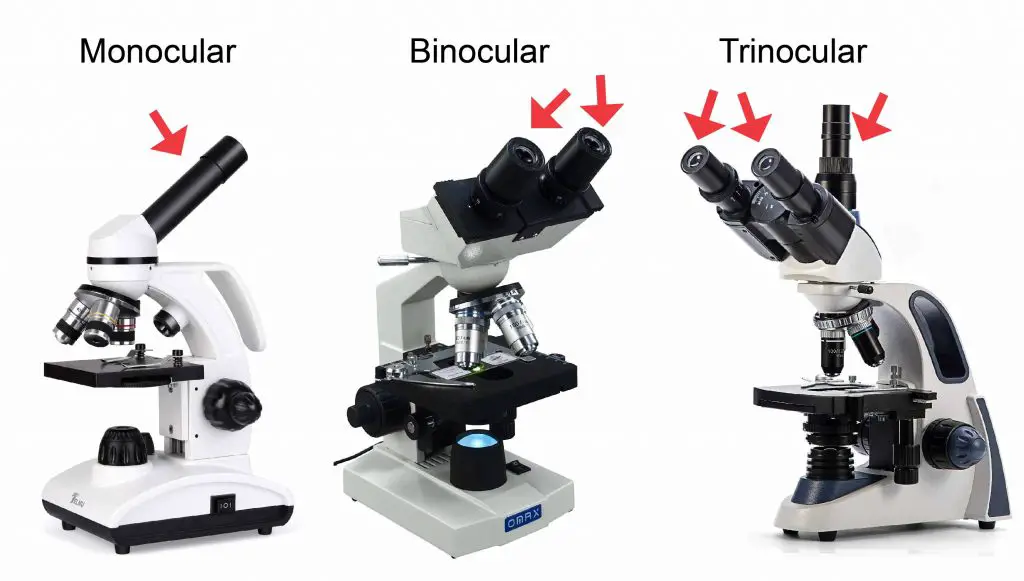
[In this effigy] Examples of Monocular, Binocular or Trinocular microscopes
iv. Iris Diaphragm & Abbe Condenser
A descent compound microscope (higher than $200) should equip with an iris diaphragm and a good quality condenser – ideally, an Abbe condenser which allows for greater adjustments. Both items are found in the sub-phase of the microscope and are used in adjusting the base illumination to ensure a uniform lightness of your microscopic images.

[In this figure] Both Iris Diaphragm & Abbe Condenser are equipped under the specimen phase
5. Accessory
Some microscope comes with a microscopic slide preparation kit that may include many accessories like slides, coverslips, test tubes, tweezer, etc. It may catch your eyes because y'all may eventually need most of this stuff. Yet, based on my personal feel, these accessories are non the best quality. I would rather purchase them according to my needs or buy a high-quality microscope accompaniment gear up.
On the other mitt, some accessories (like grit cover, maintaining tools, ability cord, and user manual) must come with the microscope. If yous tin can't observe them, contact the seller immediately! If yous look for a high-priced item, it is worthwhile to inquire the sellers to include some accessories as gifts. For case, I volition enquire for immersion oil (if your microscope is equipped with oil lens), lens cleaning paper and solution, additional lamp/LED, and extended warranty or almanac maintenance service.
6. Repair, Replacement, and Customer service
There are more details about choosing a microscope, only I don't want yous to worry as well much right at present. We will postal service our product reviews consistently on our website if y'all desire to dig more than. Nevertheless, a couple of common principles are worth mentioning here.
Brand sure you ask the seller about the policy and the process of repairing and maintenance.
Exercise they accept a technical centre near you, or yous have to ship your microscope for service?
Do they provide warranty or annual maintenance?
You may want to read the reviews about the seller'southward customer service. For a high-priced detail, choosing a well-established brand can guarantee that you tin find a professional technician to fix and extend the lifespan of your valuable microscope many years after the buy.
seven. Which Brands? Second-paw?
The compound microscopes are pretty mature products. For beginners, you lot may not need to purchase expensive microscopes from the top brands, like Zeiss, Olympus, and Nikon. Many companies (may not be equally famous as the top names) also provide high-quality microscopes at a much affordable toll.
For example, AmScope, Swift or OMAX all have decent selections from beginners to professionals. On the other paw, companies that are as well new or as well minor make me worried near customer service, repairs, and maintenance.
For the same reason, I won't recommend secondhand microscopes (you can notice many on eBay) to offset time buyers unless someone you trust is experienced and tin can help you lot with an unexpected problem.
What tin can we come across under a "Stereo" microscope?
When you will need a stereo microscope?
You will need a stereo microscope to view more substantial specimens such every bit insects, feathers, leaves, rocks, gems, coins, stamps, etc. Functionally, a stereo microscope is similar a much powerful magnifying drinking glass. Unlike a compound microscope that offers a flat image, stereo microscopes requite the viewer a 3-dimensional image that you can run into the texture of the specimen. In addition, you lot don't have to make a microscope slide for the stereo microscopes.
The proper name "stereo" comes from the term "stereoscopic," meaning, using 2 unlike angles of viewing to create an impression of depth and solidity. Because of this, true stereo microscopes simply come in Binocular and Trinocular styles. Also, different a compound microscope that can only see a very thin specimen, stereo microscopes tin can exist used for viewing almost annihilation you tin can fit under them. However, stereo microscopes offer lower magnification, typically 6.5x-45x, comparing to compound microscopes. Beneath is an example showing the difference viewing by compound vs stereo microscope.
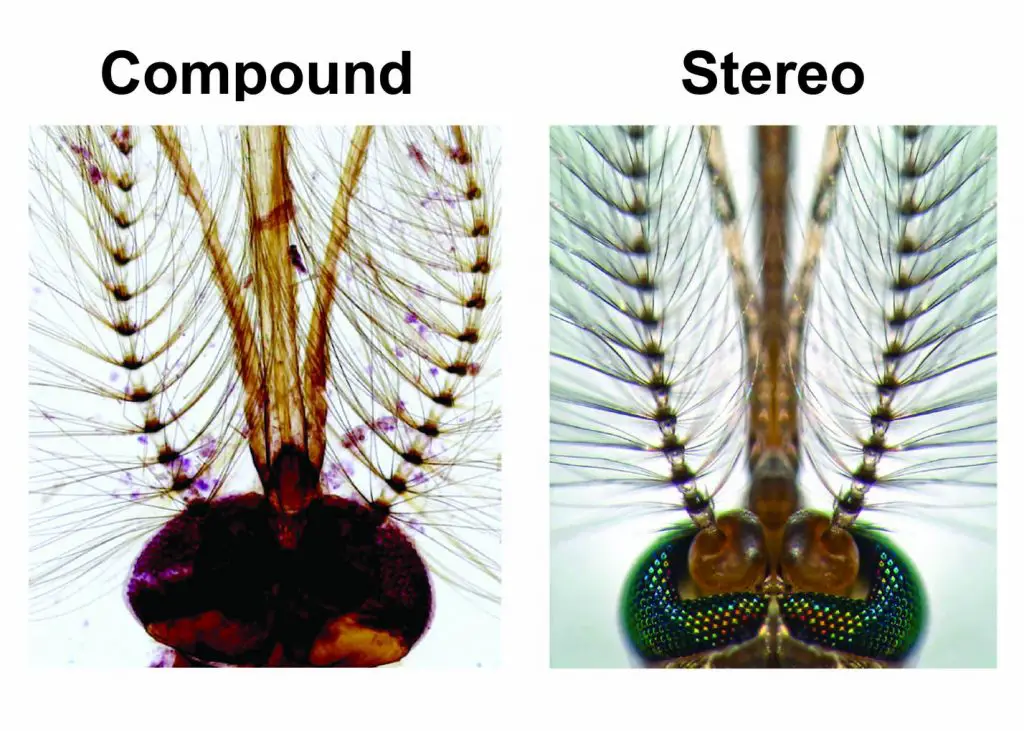
[In this effigy] Looking mosquito head nether compound and stereo microscopes.
A stereo microscope allows yous to run across the surface of specimens with a 3-dimensional view. Nether a stereo microscope, y'all can encounter the metallic texture and colors of the mosquito's chemical compound optics. In contrast, the lite has to pass through the specimen to form the epitome under a compound microscope. In this case, the region of chemical compound eyes is too thick to class a clear paradigm. Correct Image credit: Dr. Gareth Paul Jones, 2013 Photomicrography Competition, Technique: Stereomicroscopy, Cobweb Optic Illumination. Magnification: 70x.
Things to consider when choosing a Stereo microscope
1. Applications
As we mentioned in a higher place, stereo and compound microscopes are quite different. Therefore, make sure that your applications are suitable for stereo microscopes.
Stereo microscopes are particularly useful for biologists and medical doctors performing micro-dissections, technicians repairing circuit boards, paleontologists examining fossils, or anyone who needs to piece of work with their hands or tools on small objects, but large enough to exist seen or handled without the help of a loftier power compound microscope. Thus, stereo microscopes have a very wide set of potential applications across many industries.
two. Magnification
There are ii main types of stereo microscopes based on magnification — fixed ability and zoom power.
Stock-still power stereo microscopes have a set number of fixed position objectives and offer only the magnification options listed on the objectives; cipher in between. They are easy to use (you don't need to worry well-nigh focusing), but at the same fourth dimension, lack of flexibility. Sometimes, you may see a "Dual ability" stereo microscope. It ways a fixed power stereo microscope with 2 levels of magnification (commonly, 10x/30x or 20x/40x). Only rotate the objective housing to click into the desired level of magnification. The dual power microscopes are excellent starter microscopes with more affordable price, without sacrificing optic quality.
On the other manus, zoom power stereo microscopes have much greater flexibility because the objective lenses can be moved closer or farther from the specimen. This allows a range of magnification options within the maximum and minimum values of the microscope, such as half-dozen.5x through 45x. They require finer levels of refocusing when changing magnification values, therefore, making it a bit harder to use but offering much greater flexibility in terms of how much working distance, magnification, and field of view.
3. Barlow Lens
Barlow Lens is an optimal accompaniment to change the magnification power of your stereo microscope. It can work for both an increase or a subtract in magnification. For example, a 2x Barlow Lens tin double the magnification power in order to run across smaller particular. A 0.5x Barlow Lens will reduce the magnification half but enlarge the field of view (or have a wider view).
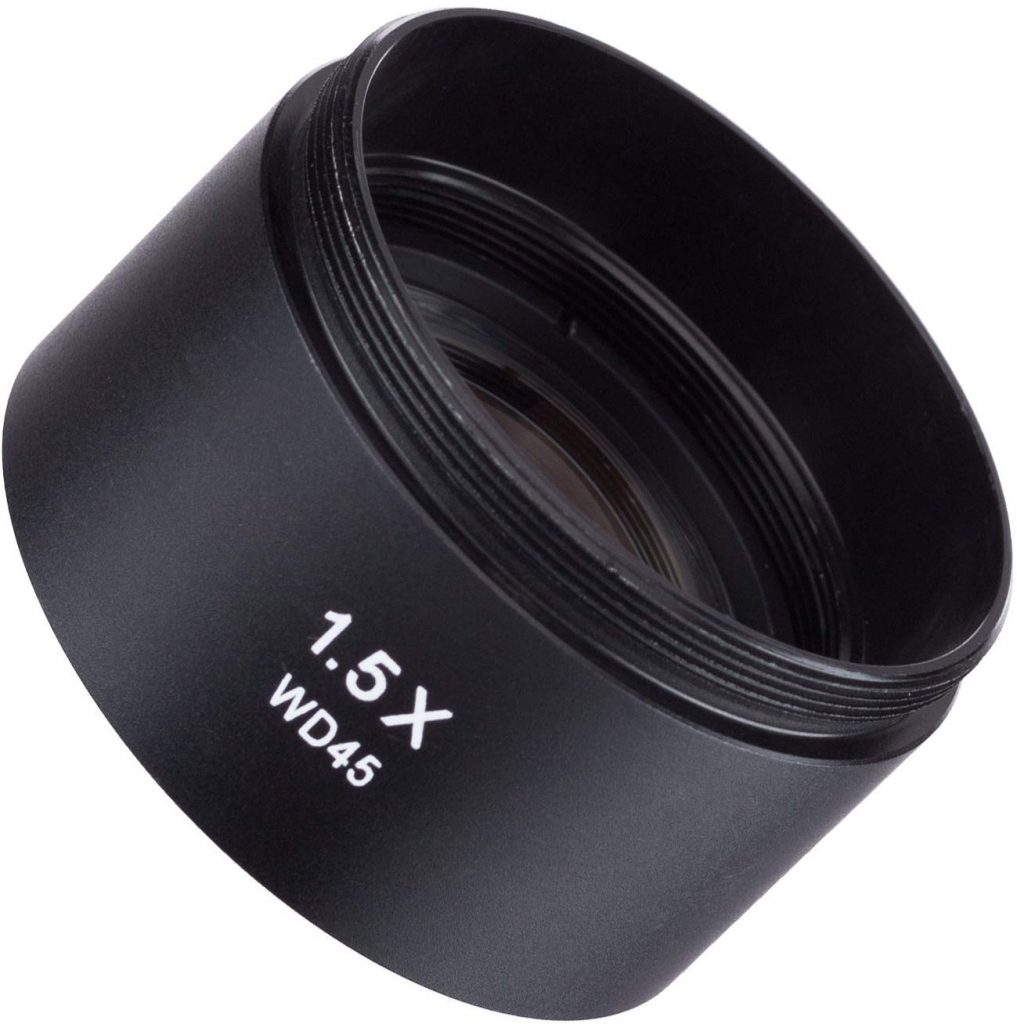

[In this figure] Barlow-Lens
four. Other considerations
Like choosing compound microscopes, pay attention to the seller'south customer service and repairs policy when y'all purchase stereo microscopes.
How about Microphotography: Cameras & Videos
When I see something amazing under the microscope, I want to document it and share the excitement with others. If you accept the same feeling as mine, welcome to the playground of Microphotography.
In that location are several solutions for capturing images and videos under either compound or stereo microscopes. For beginners with a Monocular or Binocular microscope, you lot can buy an adaptor to mount your DSLR Camera to the ocular port (afterwards removing the eyepieces). Brand sure the adaptor can fit both your camera and microscope.
Smartphone adaptors/holders are also new options. If loftier-quality images are desired, a microscope with a trinocular port is a must. Usually, the seller of trinocular microscopes volition also acquit USB or HDMI cameras as accessories. USB cameras may crave a computer to interface with and include avant-garde software capable of recording, measurement, scale, and other forms of epitome analysis. You tin can also use an adaptor to mount DSLR Photographic camera to the trinocular port, specially useful for owners of high-end cameras or professional photographers.
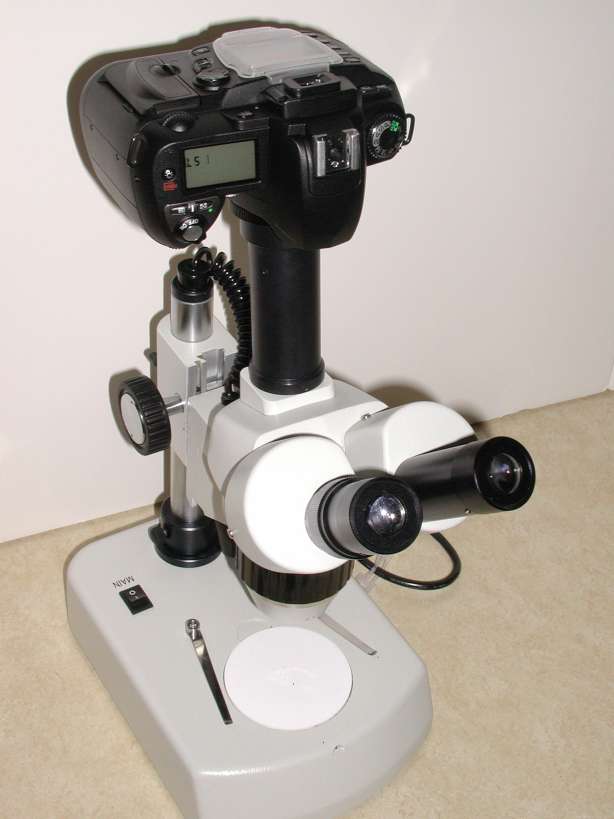
[In this figure] Mounting a Nikon D70 DSLR photographic camera to a stereo microscope.
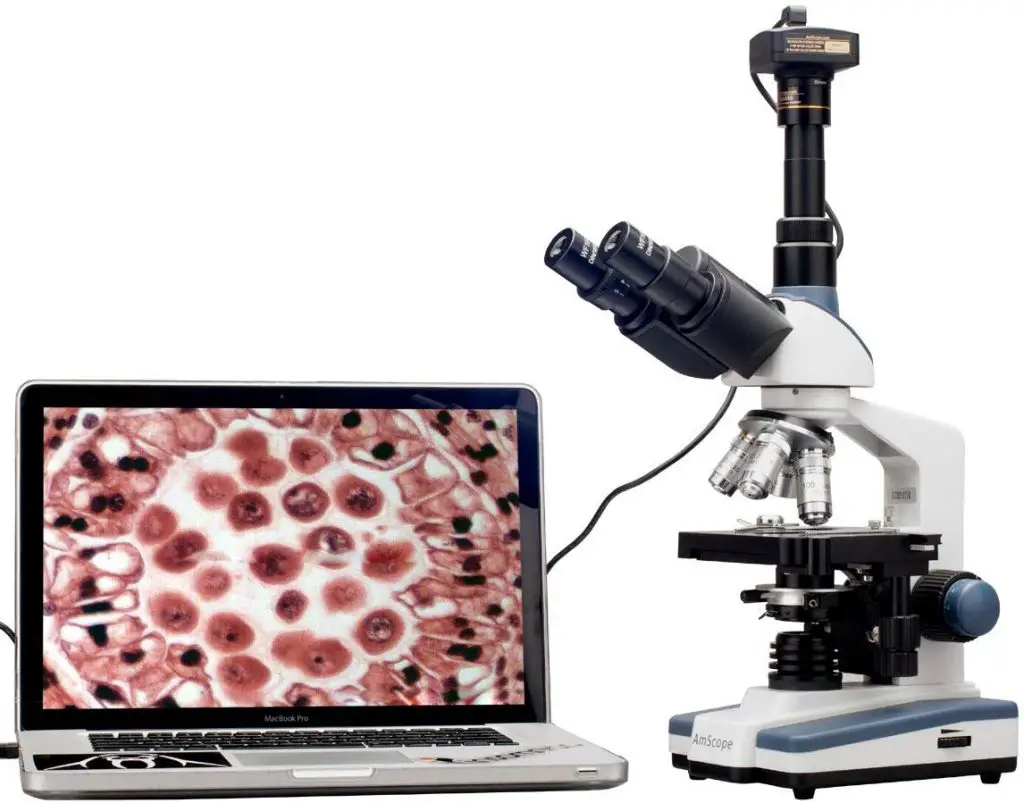
[In this figure] A parcel of Trinocular microscope with a CCD camera continued to a laptop
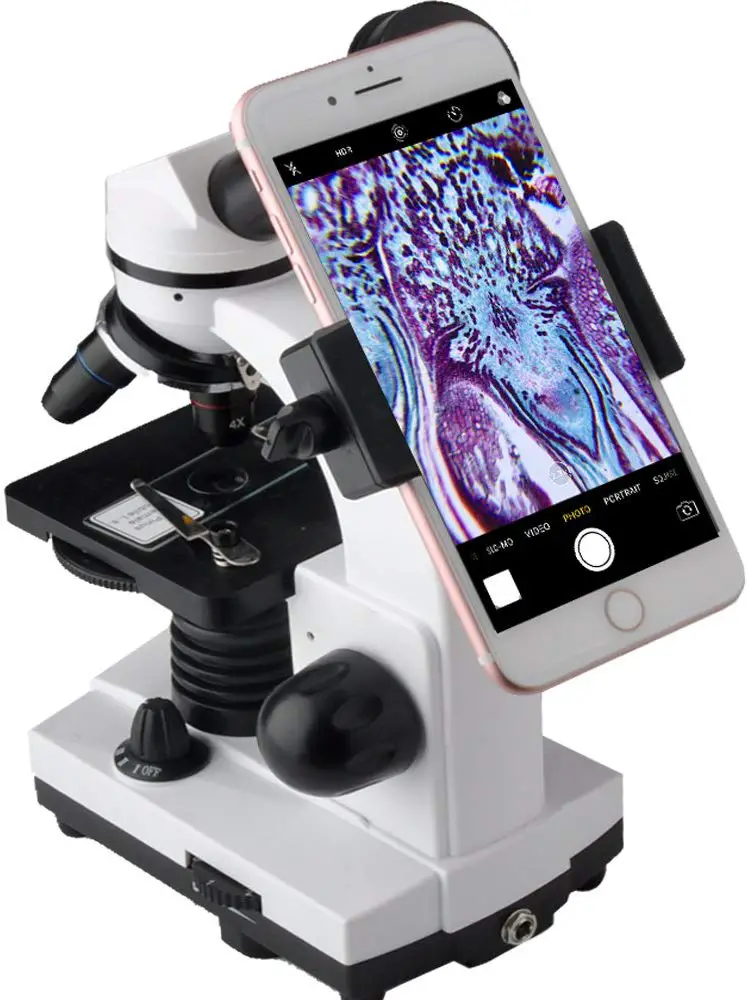
[In this figure] A iPhone holder attached on a Monocular compound microscope
Primal takeaways
Recall most your applications. What type of samples y'all would like to meet?
It's better to use a compound microscope to see something small and thin, such every bit protozoa in the pond water, blood smear (blood cells), rima oris swab (cheek cells), thin plant and tissue sections, pollens, cells, leaner, semi-transparent water organisms (like water acquit or algae) and premade slide sets. You lot can achieve much higher magnification with a compound microscope.
For the stereo microscope, suitable samples are insects, feathers, leaves, rocks, gems, coins, and stamps. Imagining the stereo microscope as a high power magnifier, you cannot reach as loftier magnification as the compound microscope. Instead, yous can encounter the 3D and the texture of the object. The image is much closer to the real object.
What would you like?
Related posts
The Beginner'southward Guide to Microscopy
Advanced Microscopy on the Frontier of Science
Stereomicroscope Vs Compound Light Microscope,
Source: https://rsscience.com/how-to-choose-the-right-microscope/
Posted by: daviswillith1981.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Stereomicroscope Vs Compound Light Microscope"
Post a Comment